Syndromes affecting the kidneys
Urofacial Syndrome
Clinical Features:
Downward slanting eyes
Downward slanting lips
Bilateral hydroureteronephrosis, which can be obstructive or non-obstructive
Genetics/Hereditary:
Likely autosomal recessive inheritance
Higher predisposition observed in Turkish populations
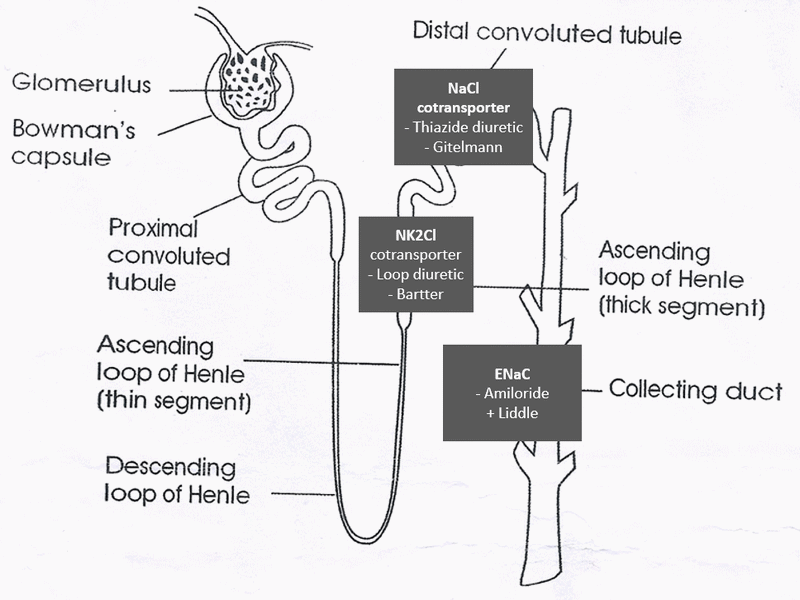
Bartter Syndrome
Pathophysiology:
Defect in the Na-2K-Cl co-transporter in the thick ascending loop of Henle (similar to loop diuretics)
Leads to NaCl wasting, hypercalciuria, and mild hypomagnesemia
Genetics/Hereditary:
Autosomal recessive inheritance
Clinical Features:
Hypotension
Secondary hyperaldosteronism
"Loop diuretics lose calcium" (Bartter syndrome mimics the effects of loop diuretics)
Gitelman Syndrome
Pathophysiology:
Defect in the Na-Cl co-transporter in the distal convoluted tubule (similar to thiazide diuretics)
Leads to NaCl wasting, hypocalciuria, and hypomagnesemia
Genetics/Hereditary:
Autosomal recessive inheritance
Clinical Features:
Hypotension
Secondary hyperaldosteronism
"Thiazides preserve calcium" (Gitelman syndrome mimics the effects of thiazide diuretics)
Liddle Syndrome
Pathophysiology:
Continuous activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in the collecting duct, leading to increased sodium absorption
Genetics/Hereditary:
Autosomal dominant inheritance
Clinical Features:
Early and severe hypertension with low renin and aldosterone levels
Hypokalaemia and metabolic alkalosis
Treatment:
ENaC inhibitors such as amiloride or triamterene
Bartter, Gitelman, and Liddle ALL cause hypokalaemia and metabolic alkalosis due to the wasting of potassium (K+) and hydrogen (H+) in response to high sodium (Na+) in the tubule
Alport Syndrome
Genetics/Hereditary:
Inheritance varies and may be:
X-linked dominant (approximately 85%)
Autosomal recessive (approximately 15%)
Autosomal dominant (approximately 1%)
Clinical Features:
Haematuria
Progressive chronic kidney disease (hereditary congenital haemorrhagic nephritis)
Sensorineural hearing loss
Various ocular abnormalities
References
Newman WG, Woolf AS, Beaman GM, et al. Urofacial Syndrome. 2013 Aug 22 [Updated 2023 Sep 28]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK154138/
Elizabeth Wan, Robert J Unwin, Stephen B Walsh, Liquorice, Liddle, Bartter or Gitelman—how to differentiate?, Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, Volume 34, Issue 1, January 2019, Pages 38–39, https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfy199
Watson S, Padala SA, Hashmi MF, et al. Alport Syndrome. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470419/